Biometric Devices
Biometric devices are instruments, designed to capture biometric data inputs including fingerprint and iris information from Aadhaar number holders for the purpose of authentication and identity verification.
UIDAI mandates usage of only Registered Devices in Aadhaar Authentication Ecosystem.
Registered Devices
Registered Devices means biometric devices that are registered with the authority. These devices carry a unique identifier and ensure data integrity by digitally signing biometric information within the device using a device provider’s key. This ensures that the data is captured live and not replayed or tampered with.
These registered devices fall under two categories viz. Discrete Devices and Integrated Devices.
- Discrete Devices: These devices require connectivity to a host device such as PC/Laptop/Micro ATM etc.
- Integrated Devices: These devices have the sensor integrated into the device package i.e. Phone/Tablet etc.
|
Discrete Fingerprint Scanner |
Iris scanner
|
|
Integrated device with Fingerprint & Iris Scanner
|
Integrated PoS Device
|
Level of Registered Devices
Level 0 Compliance:
L0 registered devices rely on the host system for encryption and use software-based key storage. They offer minimal protection against spoofing. Their functioning is dependent on the operating system, making them less secure and more vulnerable compared to L1 registered devices.
Level 1 Compliance:
L1 devices are chip-based and provide stronger security by performing encryption on-device within a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). They store keys in secure hardware elements, feature advanced liveness detection for anti-spoofing. Being OS-agnostic, they deliver higher security and reliability across environments.
UIDAI strengthened liveness detection in fingerprint devices to prevent spoofing and reduce failure rates as the capture of artificial/fake fingerprints is failed at the device level post implementation of Fake Finger Detection (FFD)
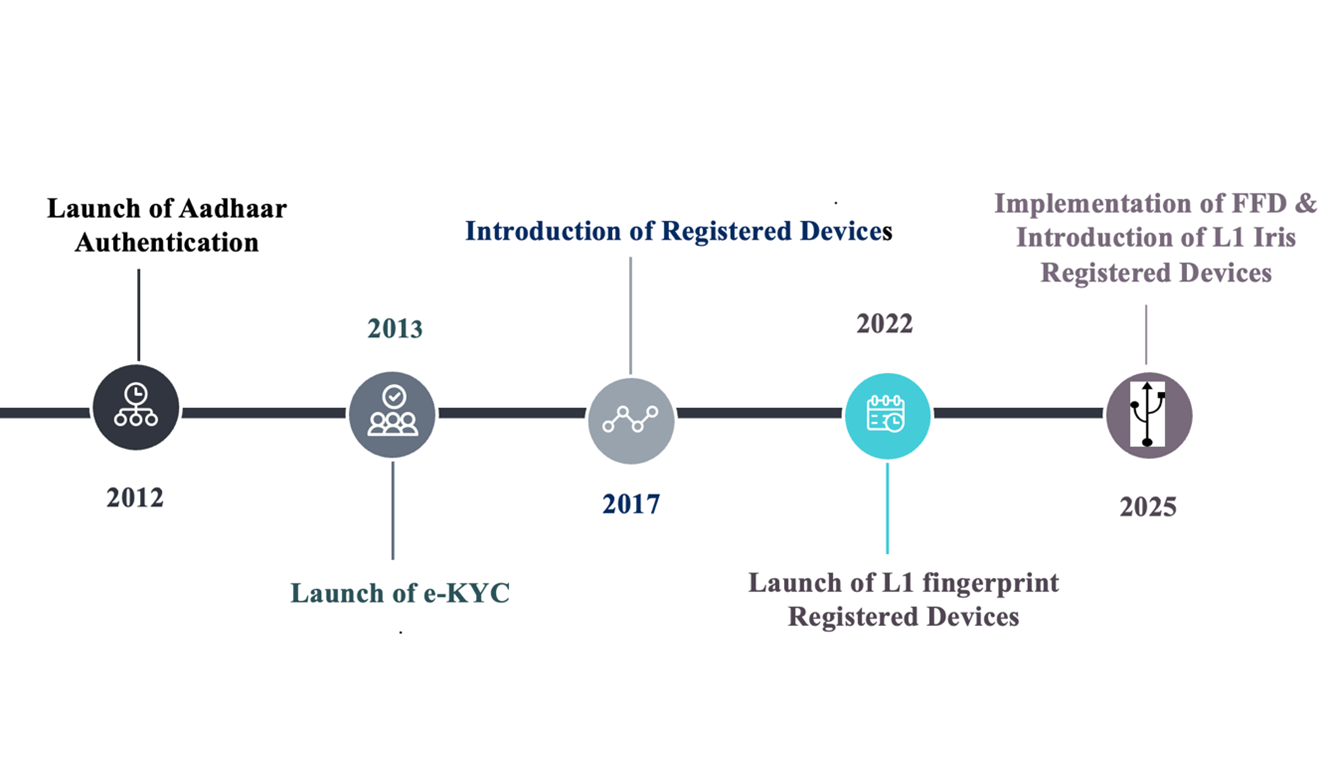
Key Milestones:
2012: Launch of Aadhaar Authentication - Laid the foundation for a secure, scalable digital identity system.
2013: Launch of e-KYC Authentication - Enabled paperless verification and ease of access to financial and government services.
2017: Introduction of Registered Devices - Enhanced security by eliminating misuse of stored biometrics.
2022: Launch of L1 Fingerprint Registered Devices - Achieved alignment with international best practices in encryption and hardware security.
2025: Implementation of Fake Finger Detection (FFD) strengthening prevention of anti-spoofing attempts in L1 Fingerprint Registered Devices and Introduction of L1 Iris Registered Devices, marking a decisive leap in trusted digital authentication.
Success Story:
Introduction of FMR-FIR (Finger Minutiae Record) based Authentication : UIDAI introduced an in-house AI/ML based model FIR to check the liveness of Finger Print.
Migration from L0 to L1 fingerprint registered devices: UIDAI has successfully migrated from L0 fingerprint registered devices to the more secure and advanced L1 fingerprint registered devices, ensuring enhanced encryption, robust tamper resistance and higher reliability in biometric authentication.