Authentication Ecosystem
Authentication Ecosystem
To be added

The Aadhaar platform provides ‘authentication’ and ‘eKYC services’ to all Aadhaar holders, on a real-time-basis. Not only is this verification service unparalleled in the world, there exist immense possibilities of its usage by National and State Government agencies, businesses and other institutions to deliver benefits, services and products, across the country instantaneously accurately and efficiently. Aadhaar authentication platform is based on a robust technology that rides on mobile connectivity and enables ubiquity. It offers a great opportunity to its stakeholders; the growing community of technology developers and the investor groups to maximize user experience in a variety of fields.
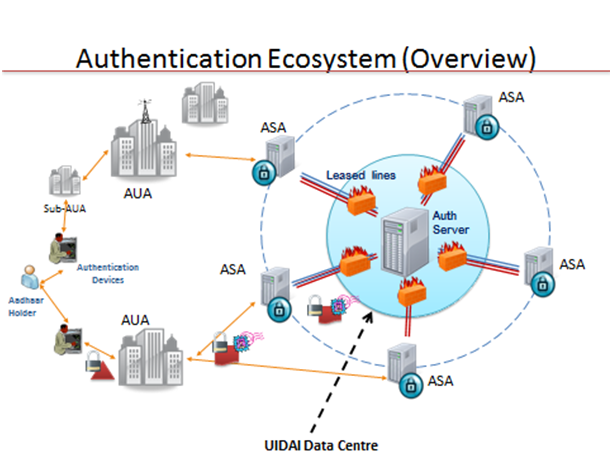
The Authentication ecosystem, shown here, contains multiple entities that work together to ensure that the authentication process is ubiquitous, accurate and efficient.
UIDAI
The Unique Identification Authority of India is at the heart of this ecosystem, and is responsible for the definition of these relationships, and the core infrastructure. It is also responsible for measuring, and monitoring the performance of the system, and driving it towards delivering on its goals. UIDAI is the overall regulator and overseer of the Aadhaar authentication system. It owns and manages the Central Identities Data Repository (CIDR) that contains the personal identity data (PID) of all Aadhaar-holders.
Authentication User Agency (AUA)
An organization or an entity using Aadhaar authentication as part of its applications to provide services to residents. Examples include Government Departments, Banks, and other public or private organizations. All AUAs (Authentication User Agencies) must be registered within Aadhaar authentication server to perform secure authentication.
Sub-AUA (SA)
An organization or a department or an entity having a business relationship with AUA offering specific services in a particular domain. All authentication requests emerging from an AUA contains the information on the specific SA. For example, a specific bank providing Aadhaar enabled payment transaction through NPCI as the AUA becomes the SA. Similarly, a state government being an AUA can have the health department under them as the SA using Aadhaar authentication while providing healthcare benefits.
Authentication Service Agency (ASA)
An organization or an entity providing secure leased line connectivity to UIDAI’s data centres for transmitting authentication requests from various AUAs. All connections to production authentication servers must come through private and secure connection through ASAs. Those AUAs who wish to provide their connectivity can become their own ASA whereas smaller AUAs who do not wish to create direct leased line connection to UIDAI’s data centres can use an ASA.
Terminal Devices
Terminal devices are devices deployed, operated and managed by by SAs/AUAs (both government and non-government) to provide services to the residents. Examples include Micro ATM devices, PoS devices, PDS terminals, and MGNREGA terminals, and Access Security devices. These devices will host the applications of the SA/AUA and support biometric capture mechanism to capture biometrics of residents for authentication purposes. The devices that collect PID (Personal Identity Data) from Aadhaar holders, transmit the authentication packets and receive the authentication results. Any additional features of these terminal devices would depend on specific needs of services offered by SAs/AUAs. These devices must comply with specifications issued by UIDAI to protect all the biometric and demographic information provided by the residents.
Aadhaar holders
These are holders of valid Aadhaar numbers who seek to authenticate their identity towards gaining access to the services offered by the AUA.
Operators
These are employed by the AUA/SA to use Terminal Devices for Authentication of the beneficiaries /residents for delivery of services/benefits and manage the service delivery points. The operators are responsible for the adherence to process and exception management. Operators must have Aadhaar numbers and should be trained before they can handle Aadhaar authentication operations.
Training Content Development Agencies
The UIDAI has engaged Content Development Agencies(CDA) to develop training materials for developers /operators. These agencies use the documentation, and new client releases to create training materials, including computer based training materials. The training materials for each release are available to the enrolment agencies and others from the UIDAI website.
Biometric Device Certification
STQC (Standardization Testing and Quality Certification Directorate), an attached office of the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Government of India, is the nodal agency appointed to carry out specifications as well as certification activity for enrolment and authentication devices requirements for the UIDAI. All the device specifications are hosted on STQC website and extensive certification activities are carried out at STQC labs at Mohali and New Delhi, which are equipped with state of art equipment to test and certify biometric devices. For more information, refer to STQC website.
Authentication Factors
Aadhaar authentication will support authentication using multiple factors. These factors include demographic data, biometric data, OTP or combinations thereof. Adding multiple factors may increase the strength of authentication depending on the factors. Applications using Aadhaar authentication need to choose appropriate authentication factors based on the application needs.










 play_circle_outline
play_circle_outline
 play_circle_outline
play_circle_outline
 play_circle_outline
play_circle_outline
 play_circle_outline
play_circle_outline
 play_circle_outline
play_circle_outline

